Ex.3 PLASMA-BASED COATINGS PROCESSES FOR NANOCOMPOSITE MATERIALS
CONTACT : JEAN-PASCAL BORRA
Synthesis of gold NP@polymer nanocomposite (NC) coating, by metal salt NP reduction with simultaneous polymerization of evaporated monomer in DBD (2021-25, ANR PLASSEL, [2])
Different options have been tested for deposition of NC polymer films on large areas with DBD. Most use a liquid aerosol, i.e. droplets of liquid monomers suspended in a carrier gas to the plasma.
For NC coatings, the injection of a liquid suspension of premade NP in a polymerizable solvent leads to NC films with NP eventually aggregated. Otherwise, synthesis of NP by plasma reduction of a metal precursor is investigated with a dissolved/crystalized Gold salt injected in DBDs.
This ANR project highlights the interest of atmospheric pressure DBD for one-step and safe-by-design Aerosol-Assisted plasma synthesis of Nano-Composite (NC) polymer films, containing 5 to 50 nm Au NP. Indeed, Metal@polymer NC films have been processed with Gold NP, for plasmonic properties.
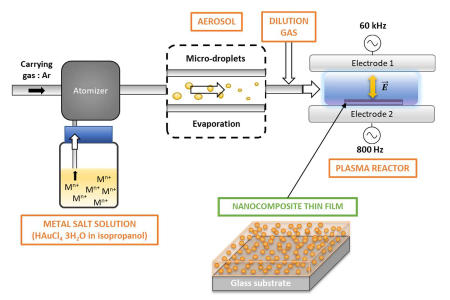
A solution of Gold salt in isopropanol- (HAuCl4, 3H2O) is first nebulized into 0,3 µm droplets suspended in Ar. Aerosol size distribution measurements support fast evaporation before injection into the DBD of solid salt nanoparticles (NP) of about 30 nm diameter with eventual traces of solvent.
1) Pt- catalytic NP production by spark-surface interaction, followed by 2-3) post-DBD Reactive Nucleation also called PE-CVD ; (right) size distributions of Pt- NP from sparks only, compared with the same coated aerosol with DBD on for 2 TEOS concentrations
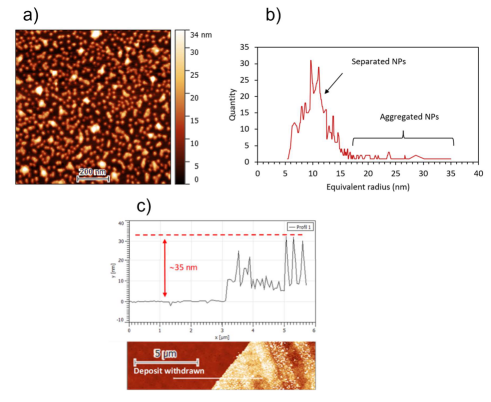
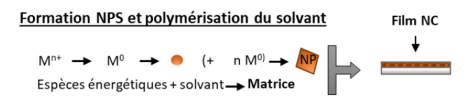
Fig: (left) Set-up for NC coating by AP-PECVD, where metal salt solution is nebulized as a liquid aerosol, ie as droplets suspended in Ar flow injected in DBD, and (Right) AFM of a NC film from Ar DBD; a) topography of the coating b) grain size distributions inferred from AFM image analysis and c) scratch test profile measured on the white line of the scratched sample image. (Bottom) mechanism of NP and polymer formation by reduction of Au3+ salt NP and simultaneous has phase polymérisation of evaporated isopropanol
Size distributions at several positions between the atomizer and the plasma support that:
this liquid aerosol reach the DBD, as 30-40 nm salt particles, expected from fast evaporation of initial 300 nm droplets with 1.6 mg/mL Au3+ salt dissolved in isopropanol. Hence, the aerosol injected into the DBD is made of solid crystallized salt NP suspended in Ar with traces of Isopropanol.
Morphological and chemical analyses show that the gold salt is reduced by DBD leading to Gold Metal NP, with 8nm modal diameter derived from XRD, confirming the size distribution of injected salt aerosol. The reduction of 30-40 nm Au3+ NP into 8nm, Au0 deposited NP, thus occurs in plasma on injected crystalized gold salt NP resulting from IPA evaporation.
The reduction mechanism of such suspended salt NP is under investigation (free electrons, radicals from VOC decomposition,…) to account for smaller Au° NP reported with NH3 addition in Argon.
Ammonia may also act as electron scavengers, thus competing with salt reduction and could also affect the charge and kinematics of NPs upto the substrate. Indeed, Ammonia affects plasmonic properties of these NC film, related to size, concentration and composition of embedded Au° NPs.
droplets produced by liquid fragmentation in the atomizer by pneumatic fragmentation of a solution of gold salt in isopropanol evolve in size and concentration, due to evaporation, losses to the walls and coagulation by diffusion of NP, as well as by dilution.
Laboratoire de Physique des Gaz et des Plasmas
Bat 210, rue Henri Becquerel
91405 Orsay Cedex
Tél : (33) 01 69 15 72 51
RÉSEAUX SOCIAUX


